Bangladesh Economy 2025: Growth, Challenges, and Future Outlook
Related Posts
Table of Contents
Bangladesh Economy in 2025
In 2025,
Bangladesh stands at a pivotal moment in its economic journey. Over the past decades, the nation has moved from being one of the poorest countries in the world to an emerging economy with growing global relevance. The transformation has been fueled by a combination of demographic advantages, export-driven growth, and policy reforms. As we look at the economic situation in 2025, it is crucial to analyze the key sectors, challenges, and opportunities that shape the future trajectory of Bangladesh.
Overview of Economic Growth
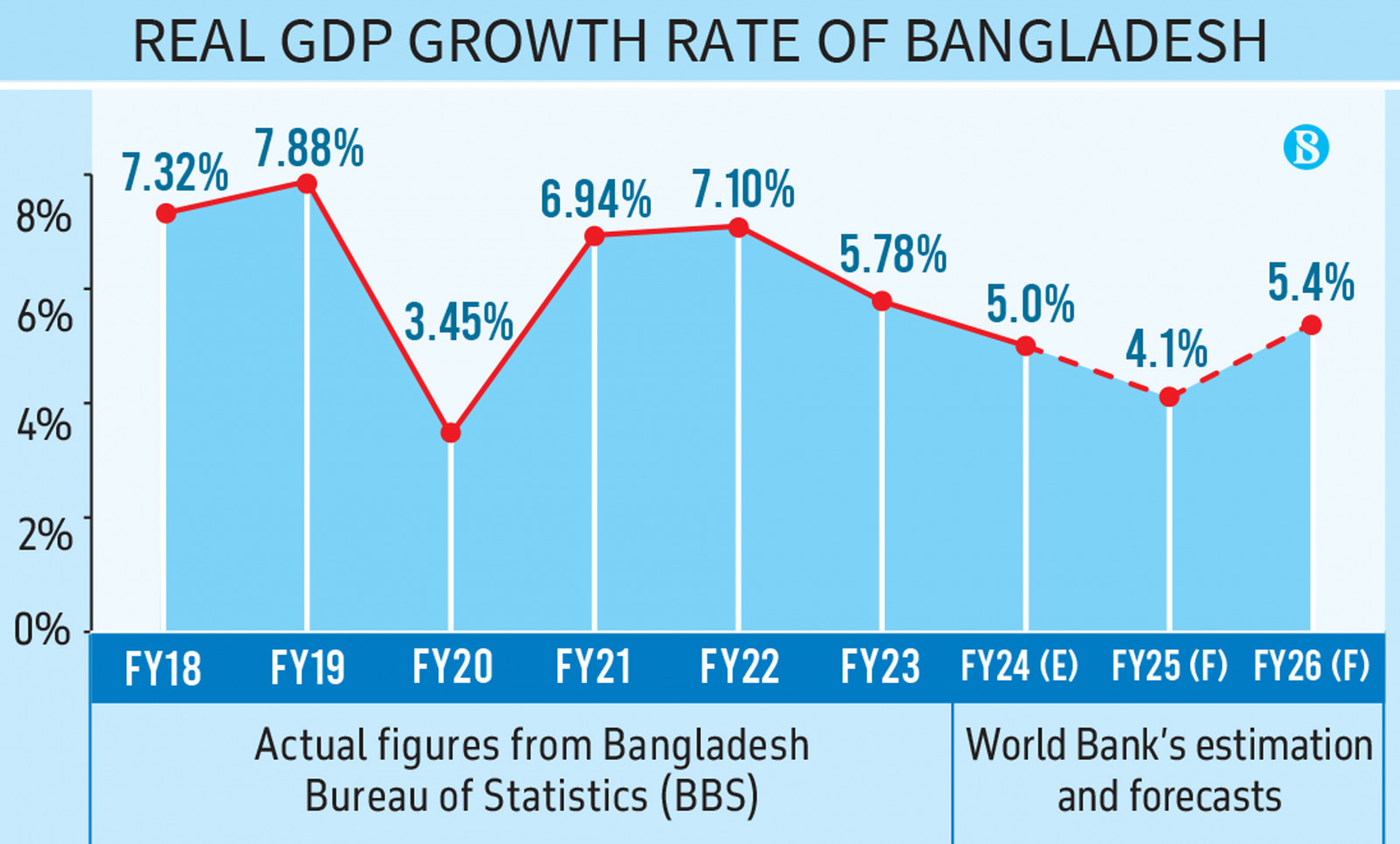
Bangladesh’s GDP growth rate in 2025 continues to hover around 6%–7%, making it one of the fastest-growing economies in South Asia. Despite global uncertainties such as inflationary pressures, energy crises, and supply chain disruptions, the resilience of the Bangladeshi economy has been remarkable. The country’s strong garment industry, remittance inflows, and expanding digital services sector are the primary engines driving growth.
GDP Trends
According to estimates from international financial institutions, Bangladesh’s nominal GDP in 2025 is projected to exceed $500 billion, placing it among the top 35 economies globally. Per capita income has crossed $3,000, reflecting a significant improvement in living standards compared to just a decade ago. The government’s Vision 2041 roadmap is aligned with this progress, aiming to transform Bangladesh into a high-income country within two decades.
Inflation and Monetary Policy
Inflation has remained a concern in 2025, largely due to higher global food and energy prices. The central bank has responded with cautious monetary tightening, raising interest rates to stabilize the currency and control price hikes. While this has curbed excessive inflation, it has also increased the cost of borrowing for small businesses.
Key Drivers of Growth
The success of Bangladesh’s economy rests on multiple pillars, each contributing uniquely to the nation’s progress. The ready-made garments (RMG) industry, information technology sector, remittances from overseas workers, and infrastructure development have all played critical roles.
Garment Industry
The garment and textile sector continues to be the backbone of Bangladesh’s economy in 2025. With exports exceeding $60 billion, the country remains the second-largest garment exporter in the world after China. Factories have increasingly adopted automation and compliance with international labor standards, improving both productivity and brand reputation. However, rising competition from Vietnam and India poses challenges, requiring continuous innovation and diversification.
Information and Communication Technology (ICT)
Bangladesh’s ICT sector has expanded rapidly, contributing over $5 billion in export earnings by 2025. The government’s "Digital Bangladesh" initiative has encouraged young entrepreneurs, freelancers, and software developers to take part in the global outsourcing market. Dhaka has become a hub for start-ups in fintech, e-commerce, and artificial intelligence applications.
Remittances
Overseas workers continue to send billions of dollars back home, making remittances a stable source of foreign reserves. In 2025, remittance inflows remain above $20 billion annually, supporting rural households and fueling domestic consumption.
Infrastructure Development
Large-scale infrastructure projects such as the Padma Bridge, metro rail systems in Dhaka, and port modernization have significantly improved connectivity and trade efficiency. These investments not only reduce logistical bottlenecks but also attract foreign direct investment (FDI).
Challenges Facing the Economy
Despite progress, Bangladesh faces a number of pressing challenges in 2025 that could undermine future growth if not properly managed. These include climate change risks, overdependence on the garment sector, governance issues, and rising inequality.
Climate Change Vulnerability
Bangladesh is one of the most climate-vulnerable nations in the world. Rising sea levels, floods, and cyclones threaten agricultural production and displace millions of people. In 2025, the government has ramped up investments in climate adaptation, but funding gaps remain a concern.
Diversification of Exports
While the garment sector is strong, overdependence on a single industry leaves Bangladesh vulnerable to global demand fluctuations. Efforts are underway to expand into pharmaceuticals, leather goods, and agro-processing, but these sectors are yet to achieve the scale required.
Governance and Corruption
Institutional weaknesses, bureaucratic inefficiency, and corruption continue to slow down investment and project implementation. Transparency reforms are being discussed, but implementation remains uneven.
Income Inequality
Although per capita income has risen, the benefits of economic growth are not equally shared. Rural areas and marginalized communities still struggle with limited access to quality healthcare, education, and employment opportunities.
Future Opportunities
Looking forward, Bangladesh has a wealth of opportunities to unlock new sources of growth. Harnessing its youthful population, green energy investments, and regional trade agreements could push the country toward its long-term goals.
Demographic Dividend
With nearly two-thirds of the population under the age of 35, Bangladesh has a significant opportunity to leverage its human capital. Investments in skills training, higher education, and vocational programs will determine whether the demographic dividend becomes a boon or a burden.
Green and Renewable Energy
To reduce dependence on imported fossil fuels, Bangladesh is investing in solar, wind, and other renewable energy sources. By 2025, renewable capacity has expanded to nearly 20% of total energy generation. This not only addresses climate concerns but also strengthens energy security.
Regional Trade and Connectivity
Bangladesh’s strategic location between South and Southeast Asia provides immense trade potential. Enhanced connectivity with India, Nepal, Bhutan, and China through road, rail, and port infrastructure could turn the country into a regional logistics hub.
Conclusion
The Bangladesh economy in 2025 is a story of resilience, ambition, and transformation. Despite global headwinds, the country has maintained steady growth and continues to make strides toward middle-income and eventually high-income status. To sustain this momentum, policymakers must address structural challenges while harnessing the opportunities of technology, demographics, and green development. With the right mix of vision and execution, Bangladesh is well on its way to becoming a significant player in the global economy.